Hello everybody,
In this series of posts we will be solving the machines related to the Hack The Box “Starting Point” labs starting with the first machine named Meow
Introduction
We will skip the process of connecting to the HTB VPN on all machines as this is a simple process which should be done with the command:
1
sudo openvpn starting_point_username.ovpn
Once the machine has been activated, it provides us with the ip 10.129.238.113, so in situations where this ip is indicated, it must be changed to the one provided by the platform.
All questions are marked with an asterisk (*) and a letter, which makes it easier to solve the task.
Tasks
Task 1
What does the acronym VM stand for?
In this case the answer is simple, Virtual Machine. If not, a quick query on google, will sort it out.
Task 2
What tool do we use to interact with the operating system to issue commands via the command line, such as starting our VPN connection? This is also known as a console or shell.
The answer is also simple, terminal.
Task 3
Which service do we use to form our VPN connection in HTB Labs?
If we check the help provided by hackthebox, we can see that the service they use is: openVPN
Task 4
What is the short name of a ‘tunnel interface’ in the output of your VPN startup sequence?
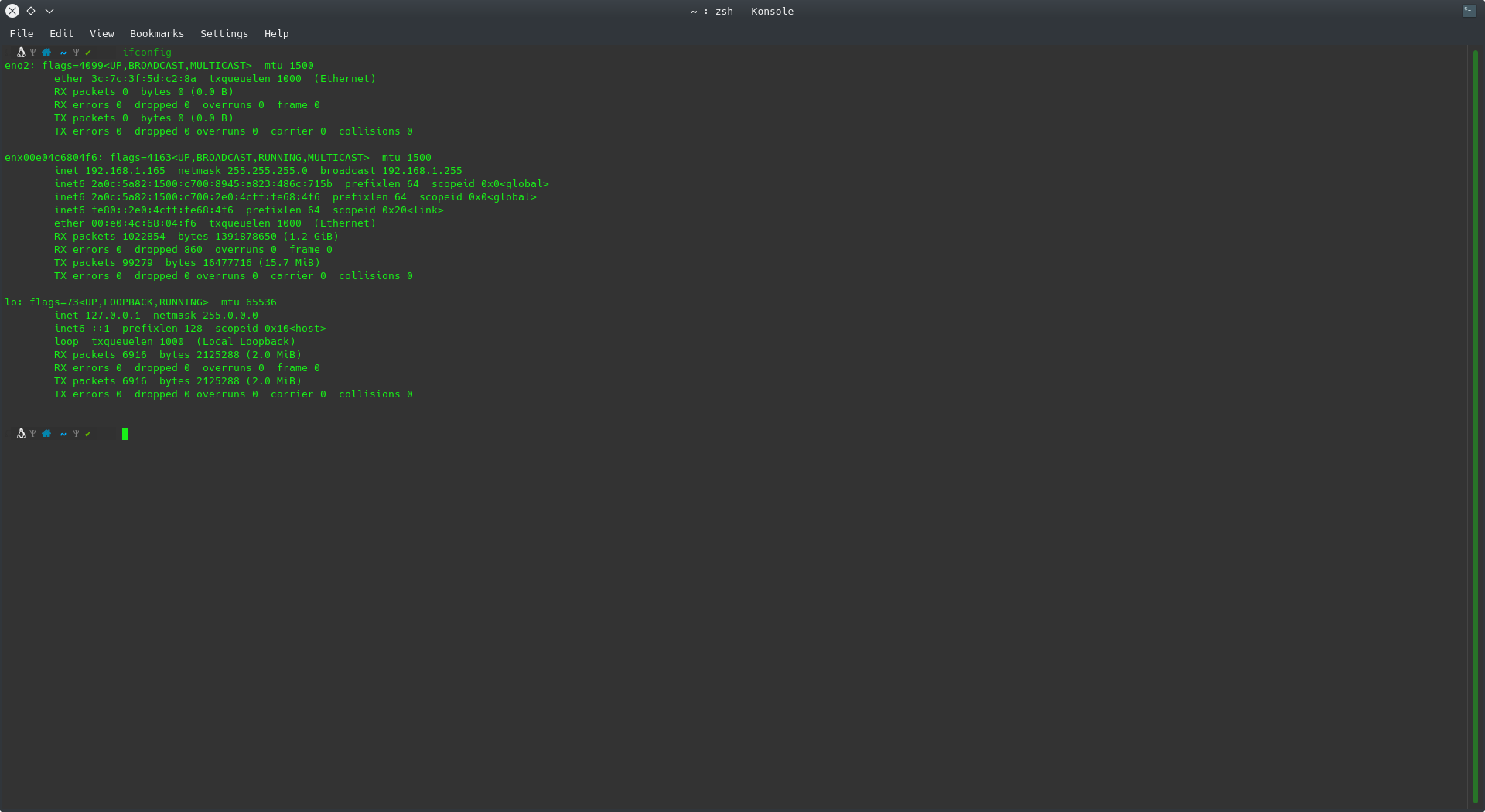
To see our network interfaces we can use the following command:
1
ifconfig
When we check our network interfaces we can see 3 interfaces:
- en02: which corresponds to the main network interface on my laptop.
- enx00e04c6804f6: which corresponds to the network interface of my hub, where I have the network cable plugged in and gives it an ip thanks to DHCP.
- lo: which corresponds to the loopback, to direct traffic to the laptop itself.
After establishing communication with the HTB VPN using the command:
1
sudo openvpn starting_point_username.ovpn
We can see that a new network interface is created:
- tun0, which is the one that manages access to the HTB network.
So the answer in this case is, tun.
Task 5
Which tool do we use to test our connection to the target with an ICMP echo request?
The default and best known tool worldwide to perform ICMP trace requests is: ping
Task 6
What is the name of the most common tool to find open ports on a target?
In this case the best known is our friend: nmap, which we will use on all or almost all targets in order to find open ports.
Task 7
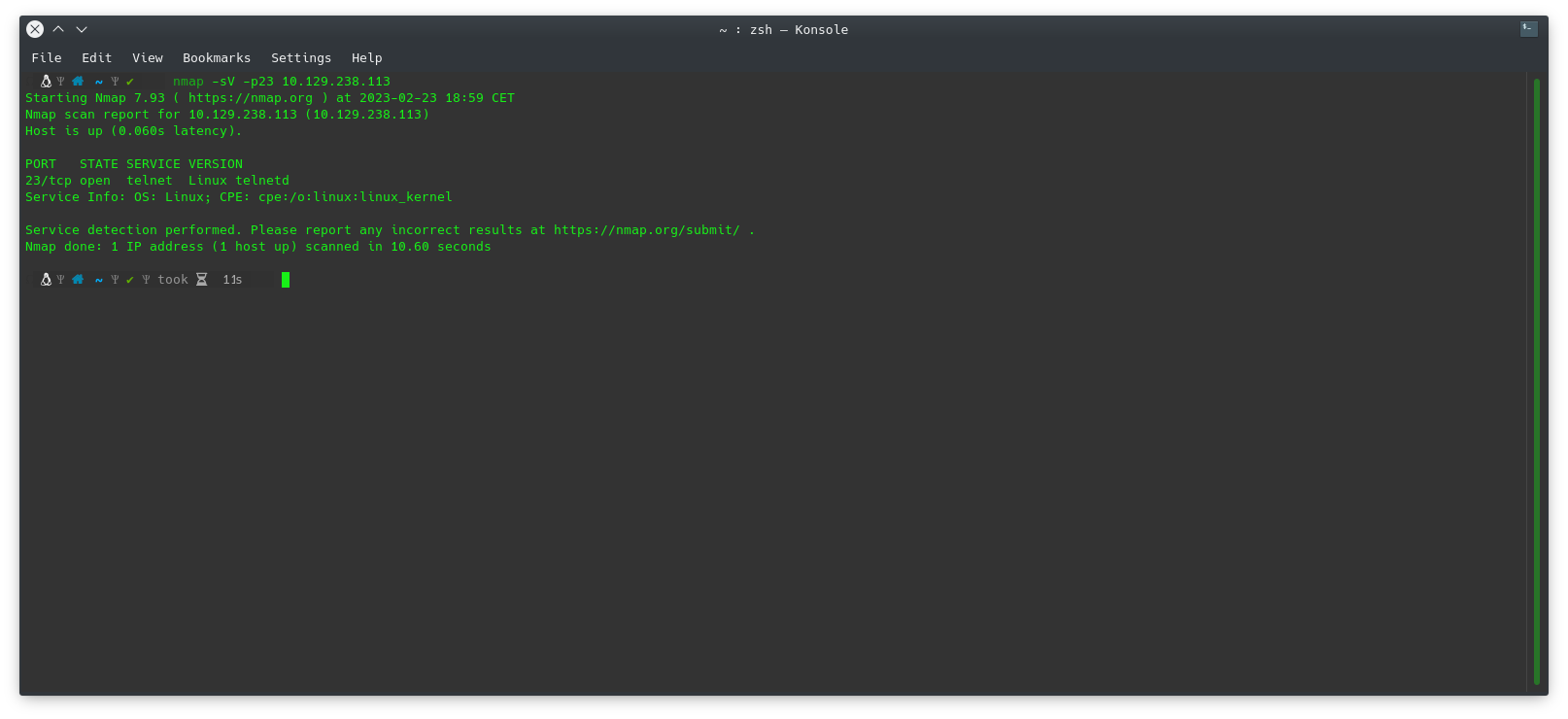
What service do we identify on port 23/tcp during our scans?
If we run nmap against the machine you have given us, we can check which service we have open:
1
nmap -sV -p23 10.129.238.113
- -sV: Allows us to find the version of the service.
- -p23: It is only used to focus on the indicated port.
In this search for services you can indicate all the ports you want, although before launching this search it would be better to find the open ports that are on the machine, to focus only on these and not delay the tool.
We can see that the service that is active on that port is:telnet
Task 8
Which user name can log in to the target via telnet with a blank password?
To find out which user can log in without a password, we can identify the most popular default usernames by using the seclist tool, where we find the following users:
- root
- admin
- test
- guest
- info
- adm
- mysql
- user
- administrator
- oracle
- ftp
- pi
- puppet
- ansible
- ec2-user
- vagrant
- azureuser
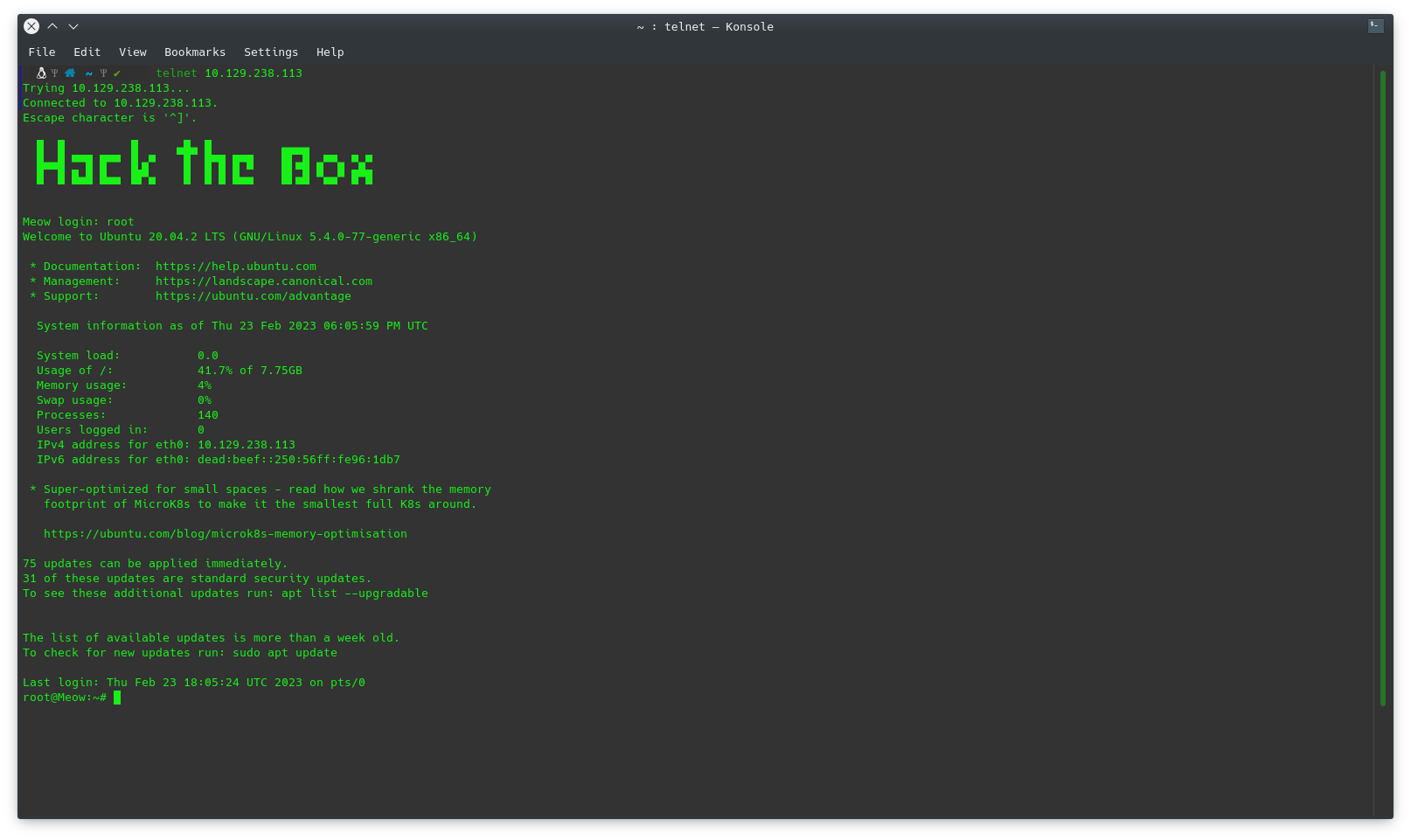
If we test the connection with the different users we can see that with the first user root we can already access.
1
telnet 10.129.238.113
Root Flag
This section asks us to obtain the flag that is “hidden” in the system.
In this case we look for the flag, which is a file containing a string of characters that must be entered and is usually hidden or privileges must be escalated to obtain it.
1
2
ls
cat flag.txt
After executing these commands it can be verified that the flag is: b40abdfe23665f766f9c61ecba8a4c19 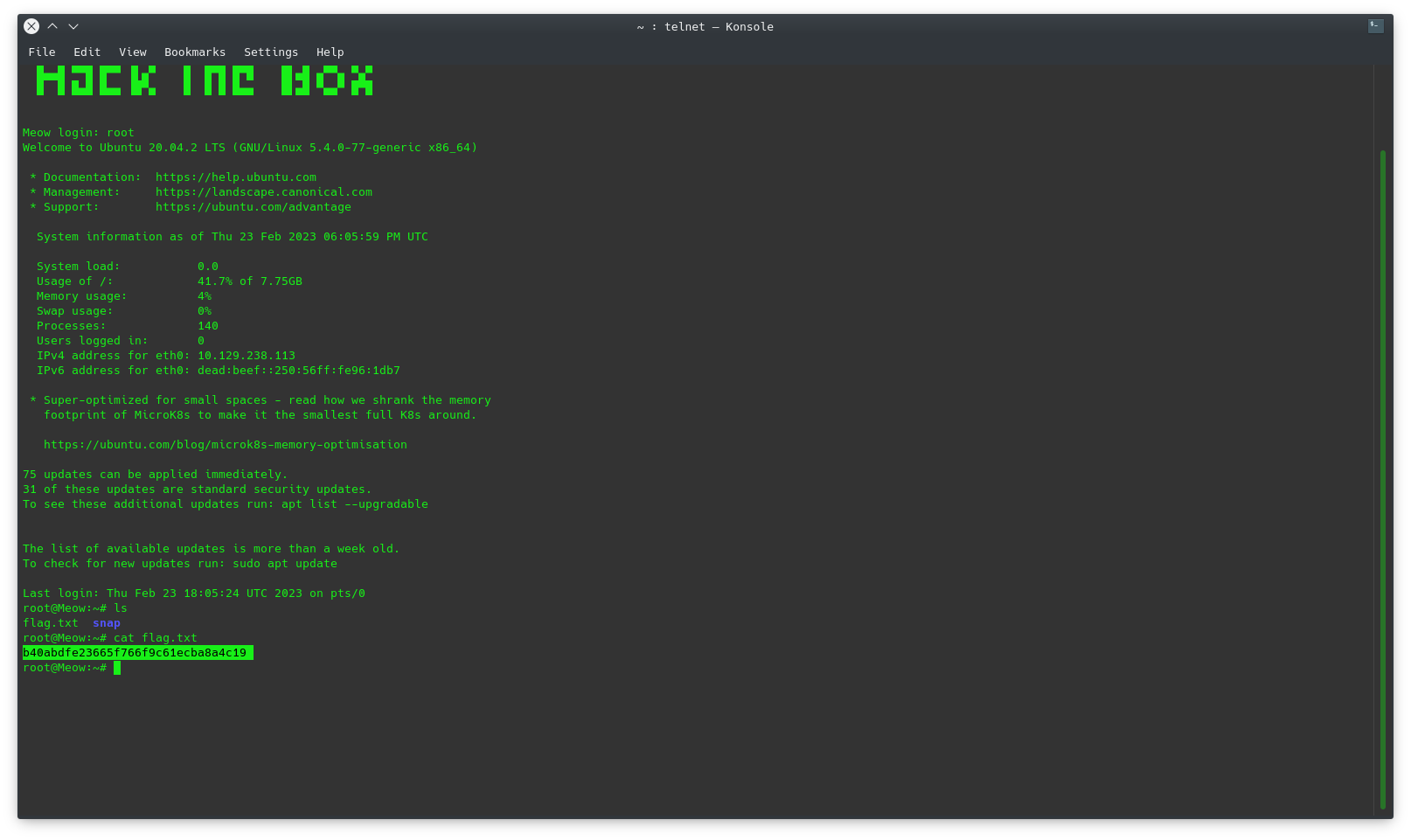 telnet
telnet
This would be all for the first machine of the HTB starting-point, I hope you liked it and see you in the next one.
Cheers.